1、支撑论文:Keer Li, Wei Chen* et al., Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 875: 159982
使用尼康MA200金相显微镜观察Ti-V合金中的kink扭折变形带。
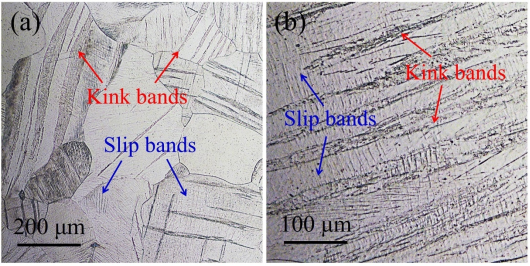
Fig. 2.Optical morphologies of Ti-18V samples after cold forging: (a) the overall image and (b) the magnification image. Kink bands and slip bands were indicated by red arrows and blue arrows, respectively.
2、支撑论文:Keer Li, Wei Chen* et al., Journal of Materials Science and Technology, Accepted
使用尼康MA200金相显微镜观察Ti-V合金中不同变形量下的kink扭折变形带的演变。
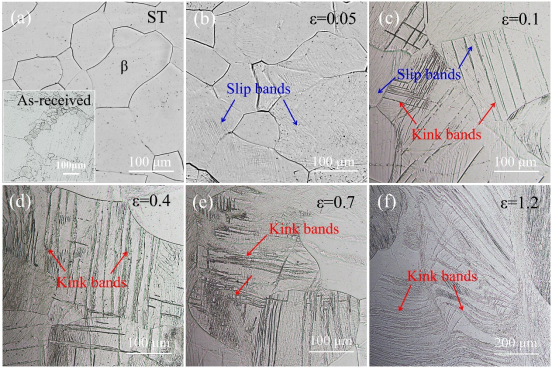
Fig. 3.Optical micrographs of Ti-12V samples cold forged to different strains: (a) the ST state. The inset shows the as-received hot-rolled morphology for comparison; (b) 0.05; (c) 0.1; (d) 0.4; (e) 0.7 and (f) 1.2. Kink bands and slip bands were marked by red arrows and blue arrows, respectively.
3、支撑论文:ZJ Lou, H Liu, GJ Yang, YH Wang, QF Yan. Microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties in the laser beam welded joints of high strength microalloyed steel. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2019, 28(6):3724-3736.
在该文章Fig 1中,利用学院Nikon MA 200光学显微镜对不同焊速条件下低合金高强钢激光焊接接头进行了表征,揭示了基体、热影响区以及焊缝区不同区域宏观组织特征的差别,为深入研究接头不同区域组织结构的差异奠定了良好基础。

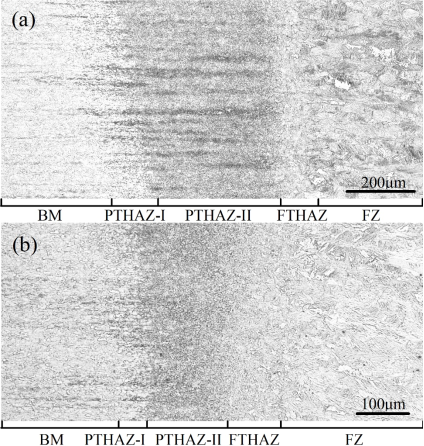
Fig. 1 Macrostructures of the high-magnification selected regions from the BM to the FZ in the welded joints at 4 kW laser power and: (a) 1 m/min welding speed; (b) 4 m/min welding speed.
4、支撑论文:ZJ Lou, H Liu, GJ Yang, YY Wen, Y Li. Effect of processing current on microstructural evolution and orientation information in Ni-based single crystal superalloy during plasma re-melting. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 861, 158589.
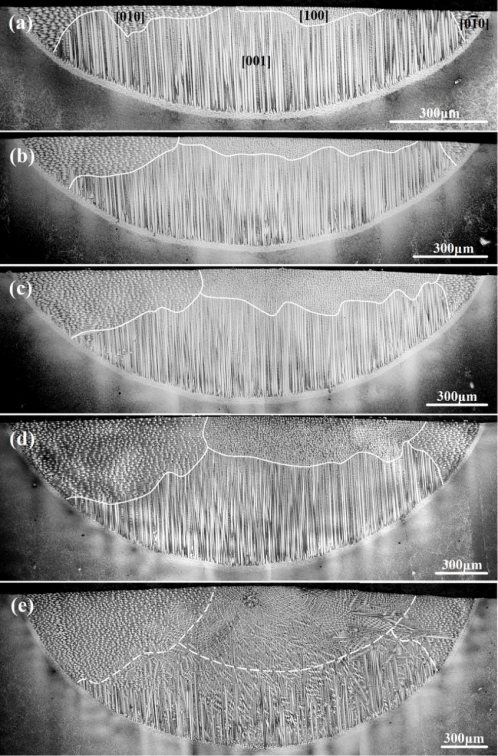
Fig. 1 Macrostructural characteristics from the BM to the FZat: (a) 25A; (b) 30A; (c) 35A; (d) 40A; (e) 45A.
在文章Fig 1中,利用学院Nikon MA 200光学显微镜表征了不同电流条件下等离子重熔镍基单晶高温合金熔化区组织特征,揭示了熔化区内晶体生长形态、不同位置晶体生长方向等特征,对于深入理解等离子修复镍基单晶高温合金过程中晶体生长行为发挥了重要作用。
5、Liu H, Shui J, Cai T, et al. Microstructural evolution and hardness response in the laser beam welded joints of pure titanium during recrystallization and grain growth[J]. Materials Characterization, 2018, 145:87-95.
本文采用Nikon ECLIPSE MA200光学显微镜对组织试样进行光学显微观察,其部分金相结果如文中的图1和图3所示。
图1显示了4kW-3m/min下工业纯钛TA2合金激光焊接接头的宏观形貌和取向信息。图1(a)为焊接接头的宏观照片,激光焊接接头由三部分组成:母材(BM)、热影响区(HAZ)和焊缝(FZ)。由图可知BM与HAZ边界十分清晰,较容易划分。而HAZ与FZ组织形态相似,其边界较难区分。图3为4kW-3m/min下充分热处理后工业纯钛TA2合金激光焊接接头的显微组织。如图3所示,经过充分热处理后BM和FZ区域的晶粒形貌并未受到明显影响,而HAZ中的晶粒则由不规则的锯齿状变为较规则的等轴状晶粒,并且晶粒尺寸明显变大。即充分热处理后HAZ区域的晶粒尺寸大于BM,并且该区域的晶粒形态明显不同于FZ。因此可利用充分热处理获得BM、HAZ及FZ的具体区域。
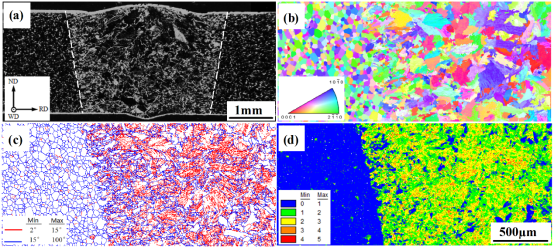
图1: 4kW-3m/min下工业纯钛TA2合金激光焊接接头的宏观形貌和取向信息:(a)宏观形貌;(b)晶粒取向;(c)晶界分布;(d)Kernel分布
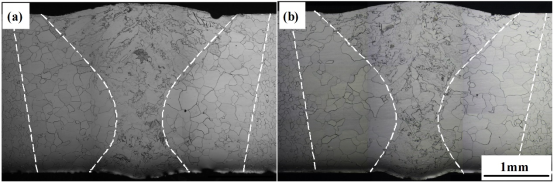 图3:4kW-3m/min下充分热处理后工业纯钛TA2合金激光焊接接头的显微组织:(a)700℃-90min;(b)700℃-120min
图3:4kW-3m/min下充分热处理后工业纯钛TA2合金激光焊接接头的显微组织:(a)700℃-90min;(b)700℃-120min
